Bariatric surgery, commonly known as weight loss surgery, is often seen as a last resort for those struggling with obesity when conventional methods such as diet and exercise have failed. But what exactly does this type of surgery involve? What are the different types, and who qualifies for them?
In this blog post, we will explore the ins and outs of bariatric surgery, including the various types, the requirements for each, and what one can expect before, during, and after the procedure. Let’s take a step towards understanding this life-changing decision.
Overview of Bariatric Surgery and its Types
Bariatric surgery is a set of procedures performed on people who have obesity. These surgical interventions work by reducing the size of the stomach or by rerouting the small intestines to a small stomach pouch (gastric bypass). There are several types of bariatric surgeries, each with its unique approach and benefits:
- Gastric Bypass: Also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, this procedure involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting the newly created pouch directly to the small intestine. This results in reduced food intake and lesser calorie absorption.
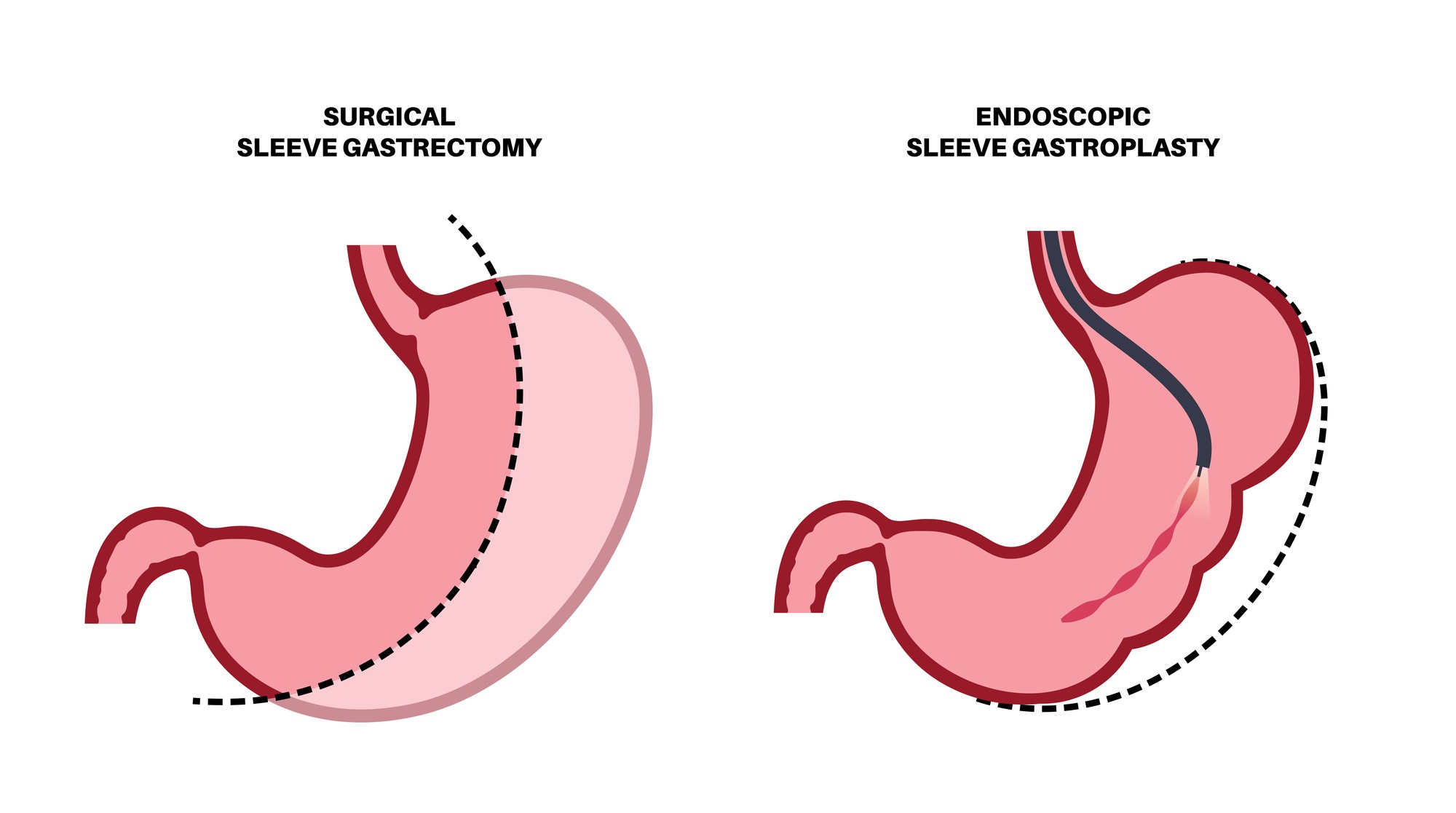
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: This procedure involves removing approximately 80% of the stomach, leaving a tube-shaped stomach about the size and shape of a banana. The result is a significant reduction in the volume of food that can be consumed
- Adjustable Gastric Band: In this procedure, a band is placed around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch above the band and the rest of the stomach below the band. The size of the passage between these two parts can be adjusted with the band
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): This is a two-part surgery, where initially, a sleeve gastrectomy is performed, and then a large part of the stomach is bypassed by connecting the end portion of the intestine to the duodenum near the stomach. This procedure leads to significant weight loss.
Exploring Benefits and Risks Associated with the Procedure
Bariatric surgery comes with an array of potential benefits as well as a set of risks, similar to any surgical procedure. An understanding of these aspects helps make a more informed decision.
Benefits:
- Significant Weight Loss: One of the most immediate and evident benefits of bariatric surgery is substantial weight loss, which is maintained over the long term.
- Improvement in Comorbid Conditions: Conditions like Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea often improve significantly after surgery, and in some cases, patients may no longer need medication.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: The surgery often leads to improved physical functioning and enhancement in the overall quality of life.
Risks:
- Surgical Complications: These can include infection, blood clots, bleeding, and reaction to anesthesia.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Due to reduced food intake and malabsorption, patients may suffer from deficiencies of vitamins and minerals.
- Psychological Effects: Some patients may experience mood disorders, such as depression or anxiety, after surgery.
Preparing for Bariatric Surgery
Preparing for bariatric surgery is a comprehensive process that involves several steps. Your medical team will provide specific instructions based on the type of surgery and your overall health condition. However, there are general guidelines that are typically followed:
- Pre-Surgery Evaluations: You’ll undergo numerous evaluations, including nutritional counseling, a psychological exam, and several medical tests to ensure you’re physically and mentally prepared for the surgery.
- Lifestyle Changes: In the weeks or even months leading up to the surgery, you’ll likely need to start making changes to your diet and exercise habits. This may include reducing calorie intake, stopping certain medications, and increasing physical activity.
- Fasting Before Surgery: Typically, you’ll need to fast (no food or drink) for a certain period before the surgery, usually starting at midnight the night before.
- Post-Surgery Follow-up: After the surgery, regular follow-up appointments will be necessary to monitor your recovery and progress. This may involve frequent check-ups with your surgeon, dietitian, and psychologist.
- Long-term Lifestyle Adaptation: Importantly, successful weight loss after bariatric surgery fundamentally requires a long-term commitment to lifestyle changes, including adhering to new dietary guidelines and maintaining regular physical activity.
Understanding Different Requirements for Bariatric Surgery
The guidelines and criteria may slightly vary depending on the hospital but generally include:
- Body Mass Index (BMI): Most weight loss surgeries are suggested when your BMI is 40 or higher (extreme obesity). In some cases, patients with a BMI between 35 and 39.9 with serious weight-related health problems can also qualify.
- Failed Weight Loss Attempts: Candidates must typically prove that they have made serious attempts to lose weight through diet and exercise but were unsuccessful.
- Comorbidities: The presence of weight-related health issues, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or severe sleep apnea, may make you a suitable candidate.
- Psychological Evaluation: A mental health screening to ensure that patients can handle the significant lifestyle changes post-surgery is often a part of the pre-surgery process.
- Commitment to Lifestyle Changes: Candidates must understand and be willing to make permanent changes to their diet and exercise habits to achieve and maintain weight loss goals.
- Age: While there’s no upper age limit for bariatric surgery, the potential benefits must outweigh the risks. For young patients, a thorough evaluation of their ability to give informed consent and handle the post-surgery lifestyle is necessary.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor Before Going Ahead with the Surgery
Deciding to have bariatric surgery is a significant step, and it’s essential to have all the information you need to make an informed decision. Here are some critical questions you might want to ask your doctor:
What are the different types of bariatric surgery, and which one would you recommend for me?
What are the potential risks and complications associated with this procedure?
How will this surgery affect my existing medical conditions?
What kind of dietary restrictions will I need to follow before and after the surgery?
What lifestyle changes will I need to make after the surgery, and how will I be supported in making these changes?
How much weight can I expect to lose, and over what period?
What type of ongoing follow-up or post-operative care is necessary?
How will this surgery affect my mental health?
What can I expect in terms of recovery time and discomfort?
What happens if I regain the weight?